Inyo National Forest
California, Nevada
Managed by U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region
2,048,459 acres (1,948,726 federal/ 99,733 other)
Website: https://www.fs.usda.gov/inyo
Overview
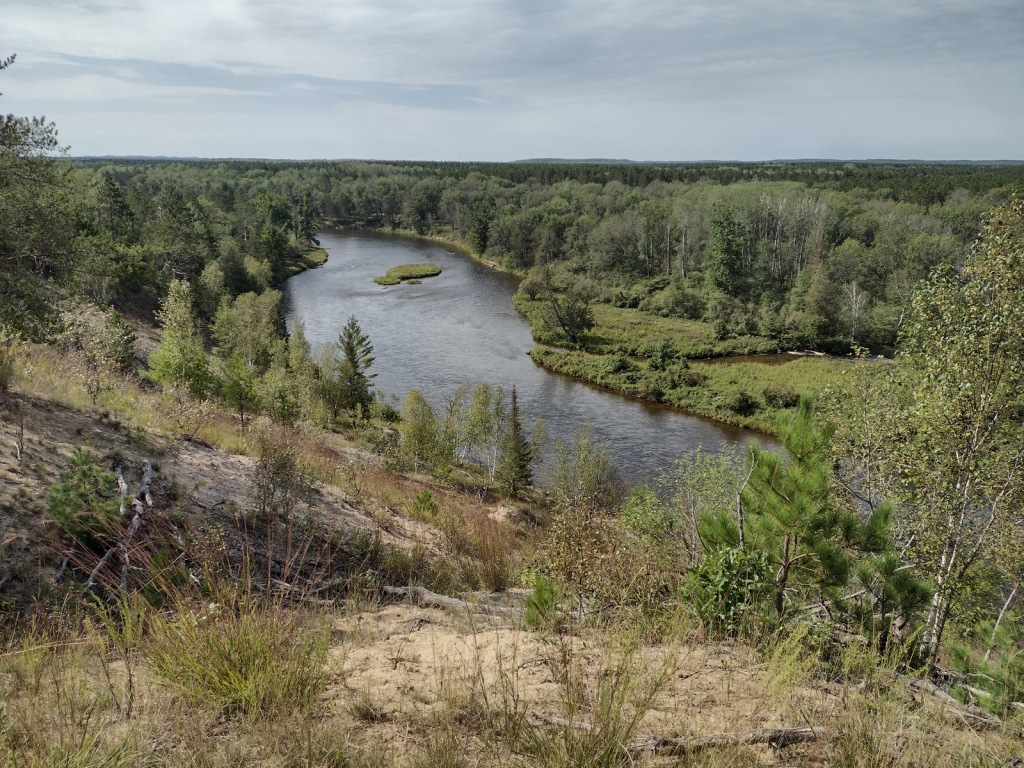
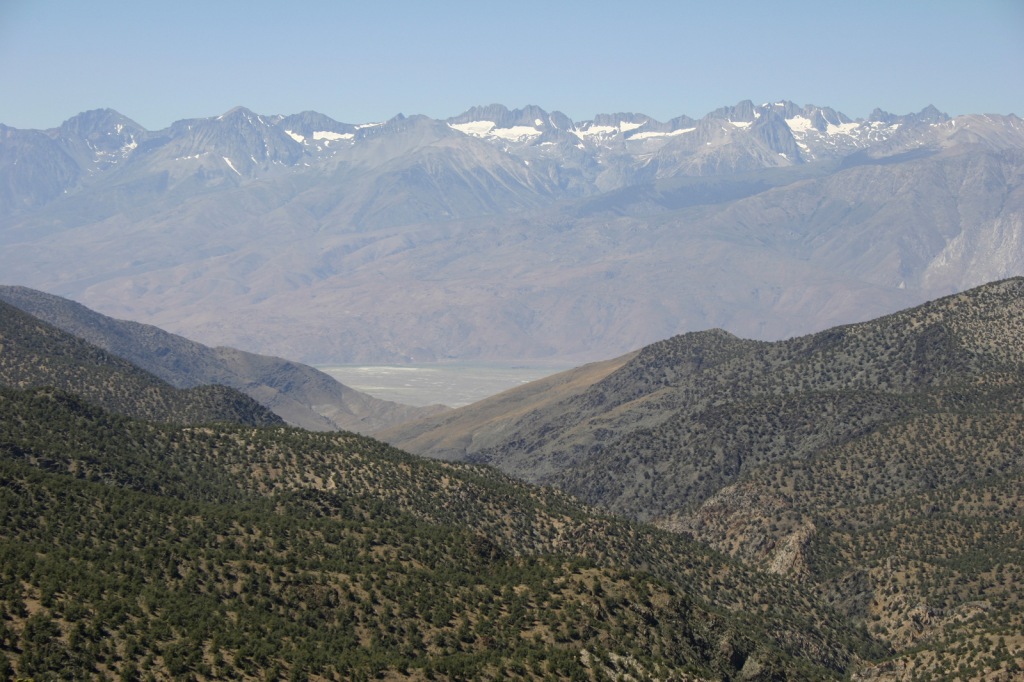
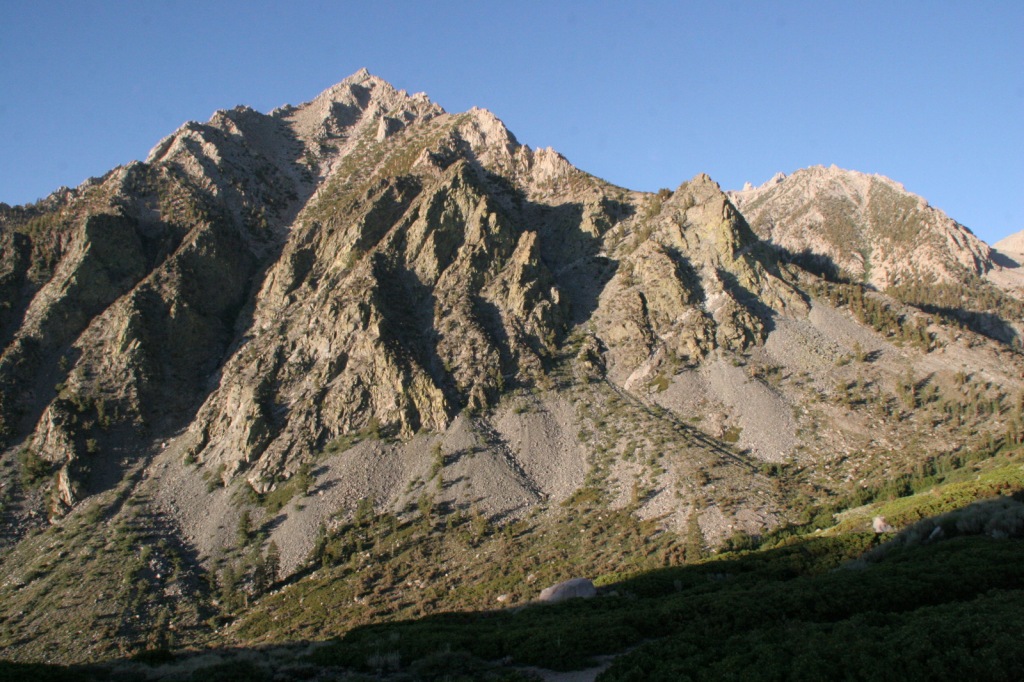
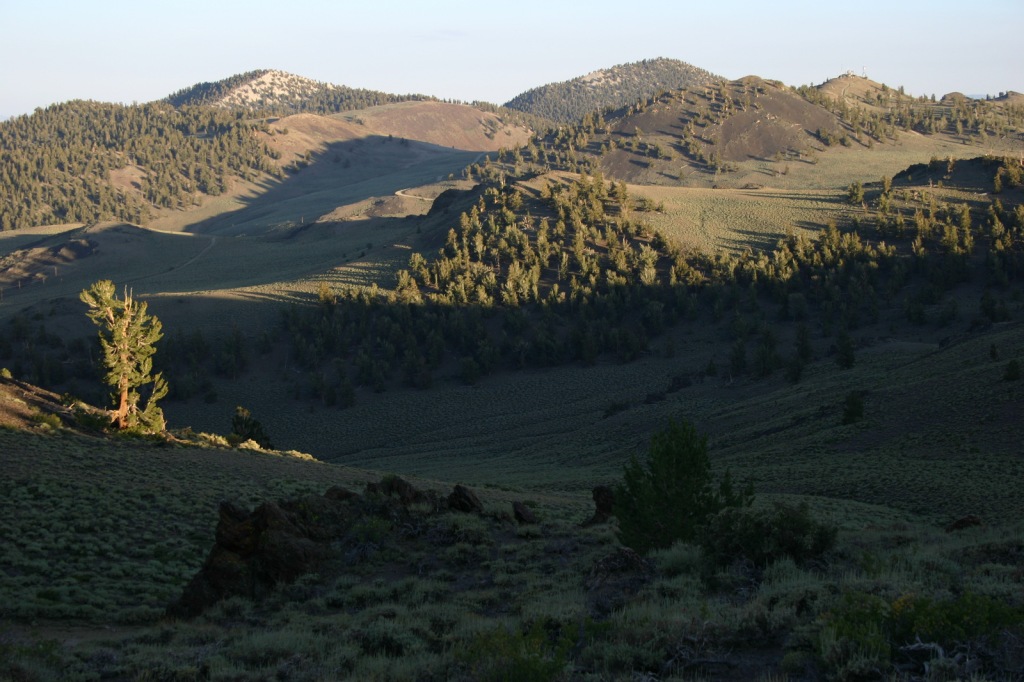
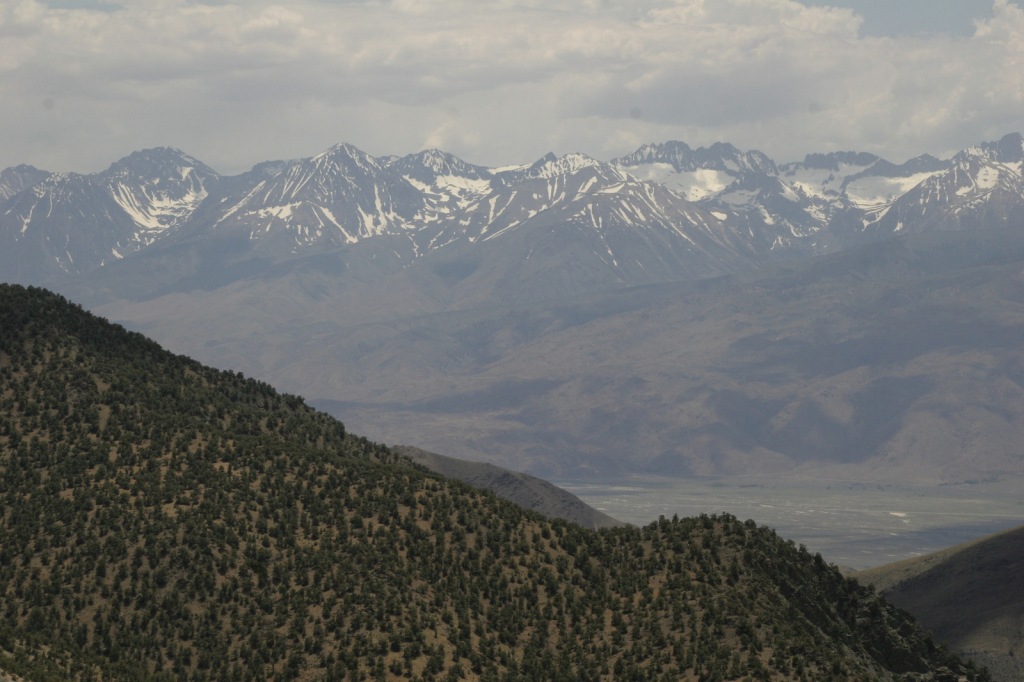
Inyo National Forest was established by President Teddy Roosevelt in 1907 to accommodate the Los Angeles Aqueduct, so it is mostly sagebrush slopes without much dense forest cover. We added it to our Top 10 Movies Filmed in National Forests after reading its history as a filming location. Inyo National Forest offers the shortest route to Mt. Whitney, the tallest peak in the contiguous U.S. at 14,495 feet in elevation. Its proximity to Badwater Basin (282 feet below sea level) in Death Valley National Park makes its rise all the more impressive. You will need a permit to summit, since this popular peak lies within Sequoia National Park. One added benefit is you will learn all about how to use a “W.A.G. bag.” In addition to accessing the eastern Sierra Nevada (see Best Trail), Inyo National Forest also offers a portal to the beautiful White Mountains along the California-Nevada border (see Must-Do Activity) and 800,000 acres of designated Wilderness.
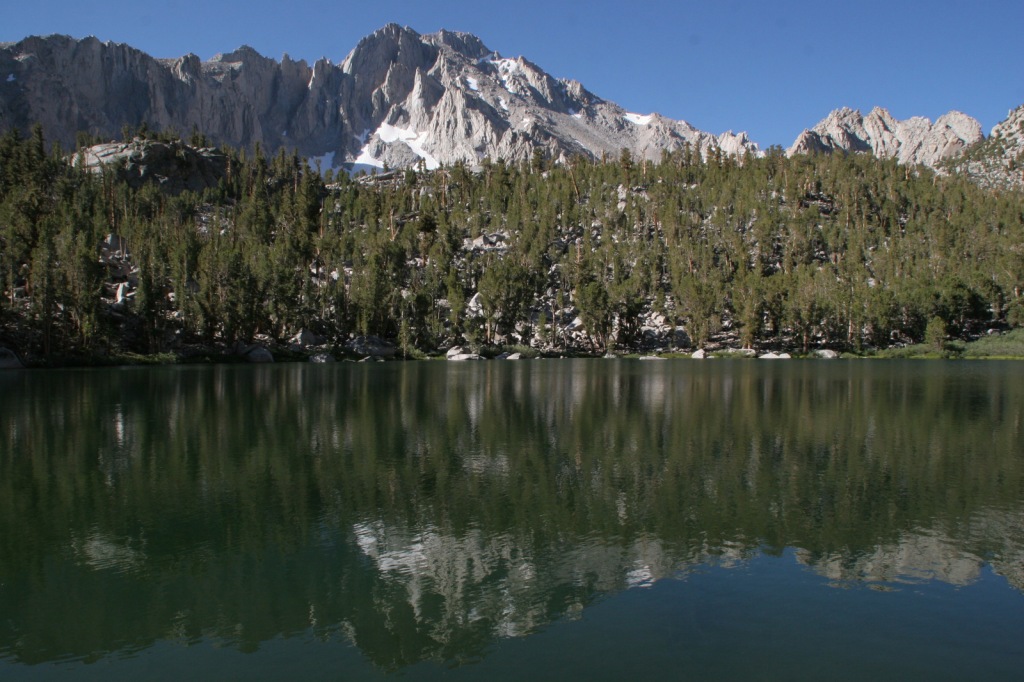

Highlights
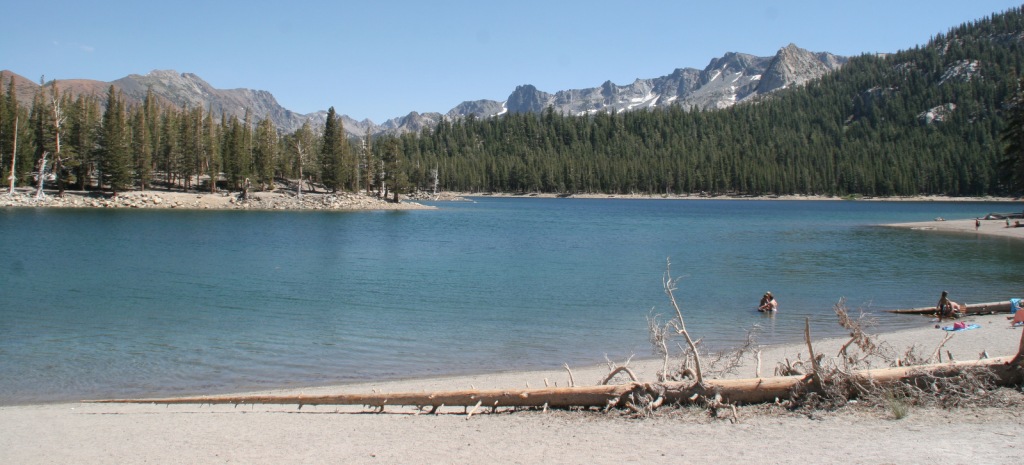
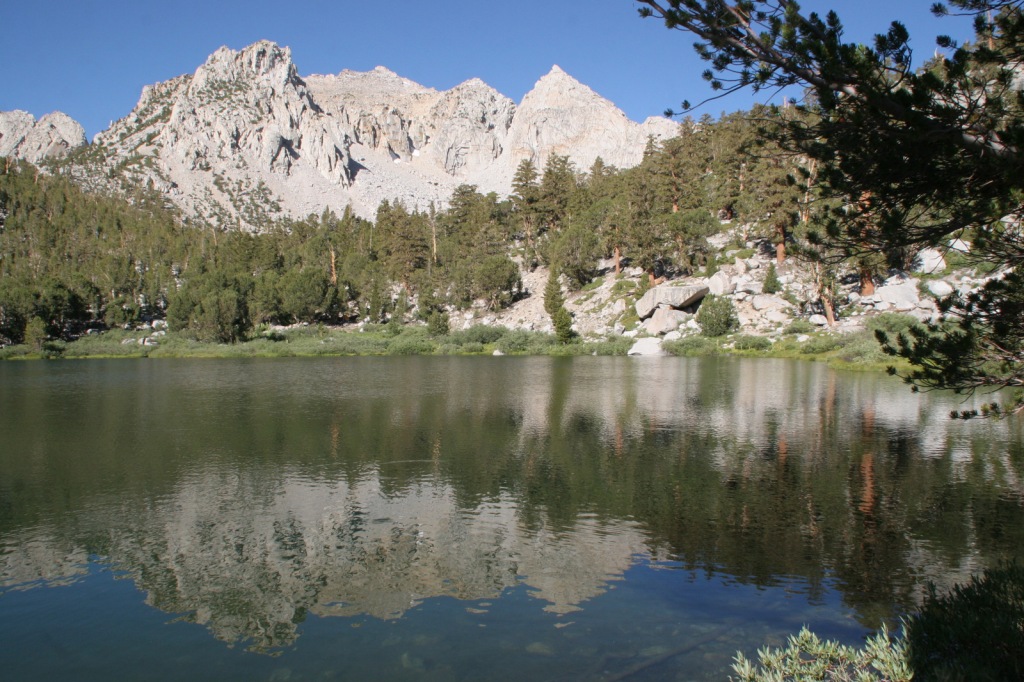
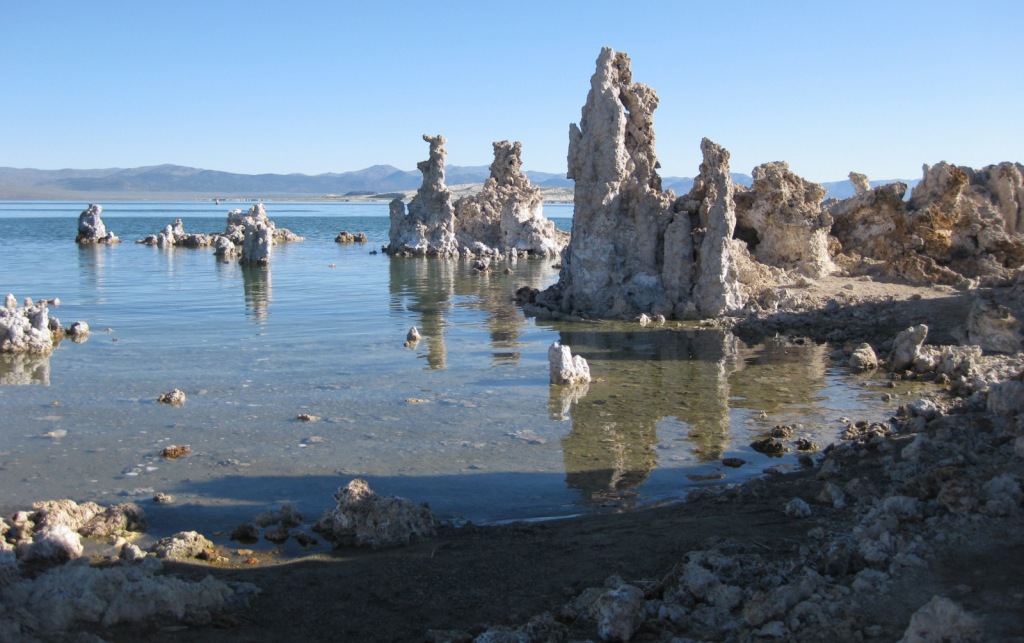
Mono Basin National Scenic Area (see our blog post), Lee Vining Canyon Scenic Byway, Tioga Pass, Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest, Convict Lake, Hot Creek Geologic Site, Mammoth Lakes, Minaret Summit Vista, Crystal Lake, Mt. Whitney Trail, Minaret Falls, Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail
Must-Do Activity
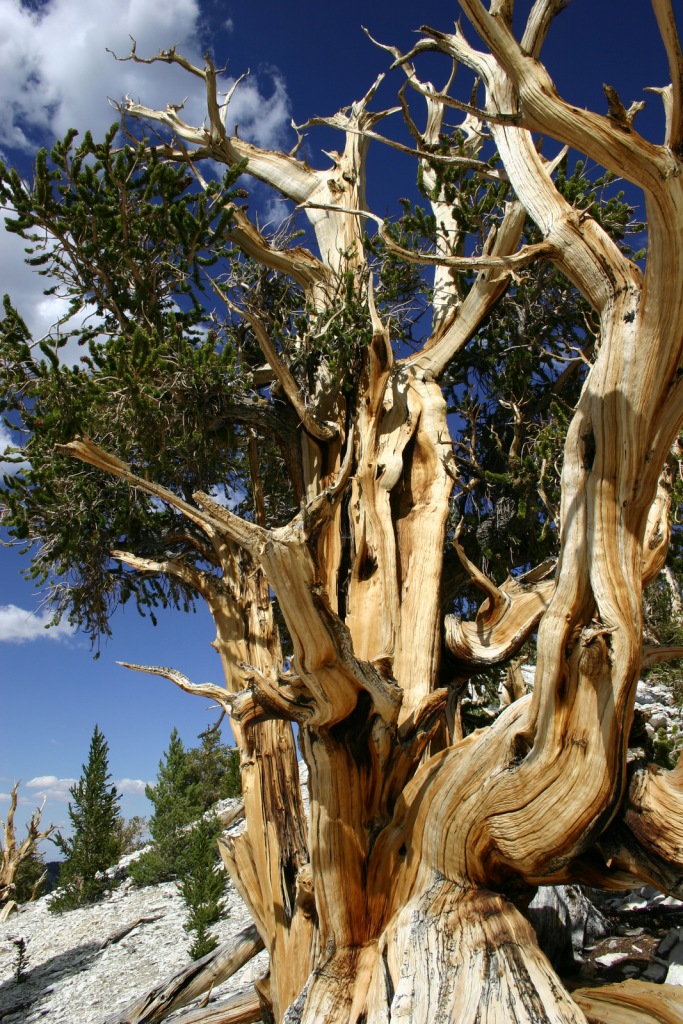
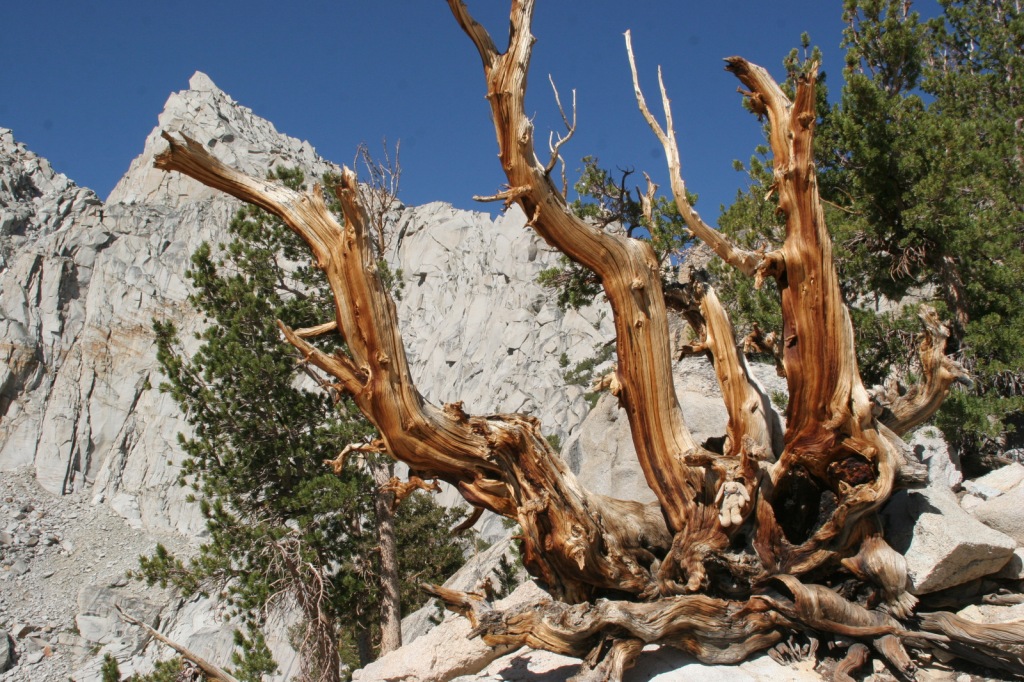
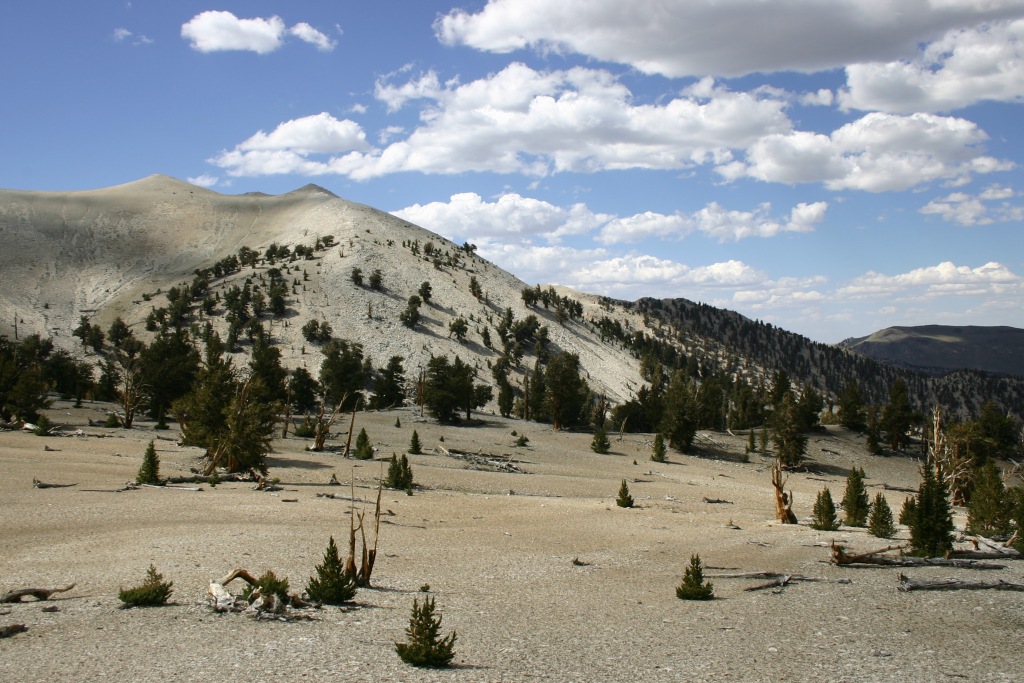
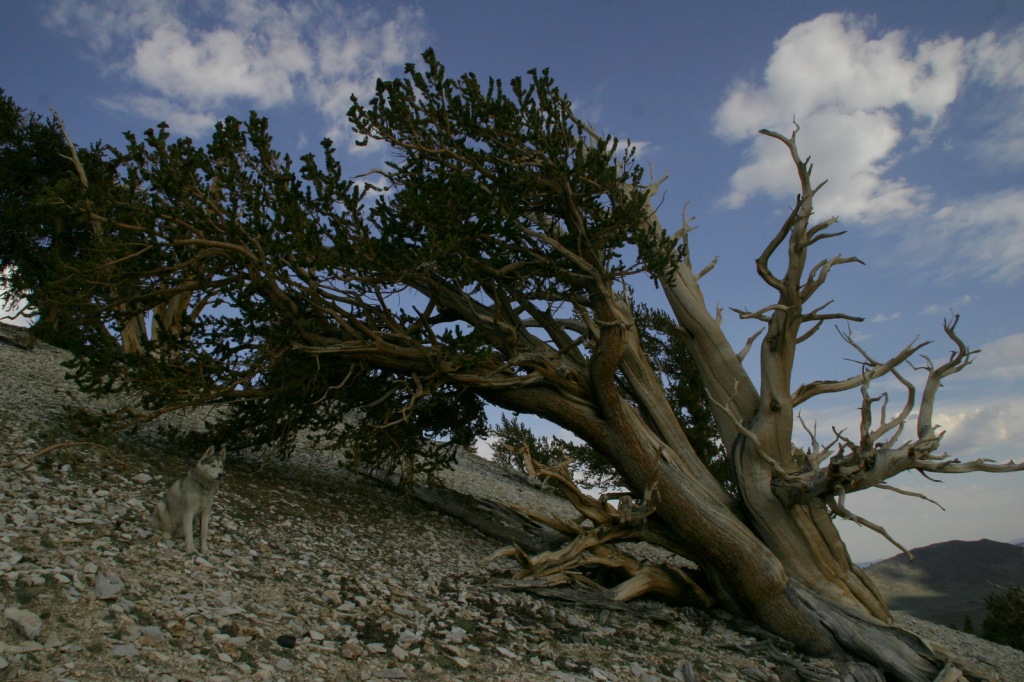
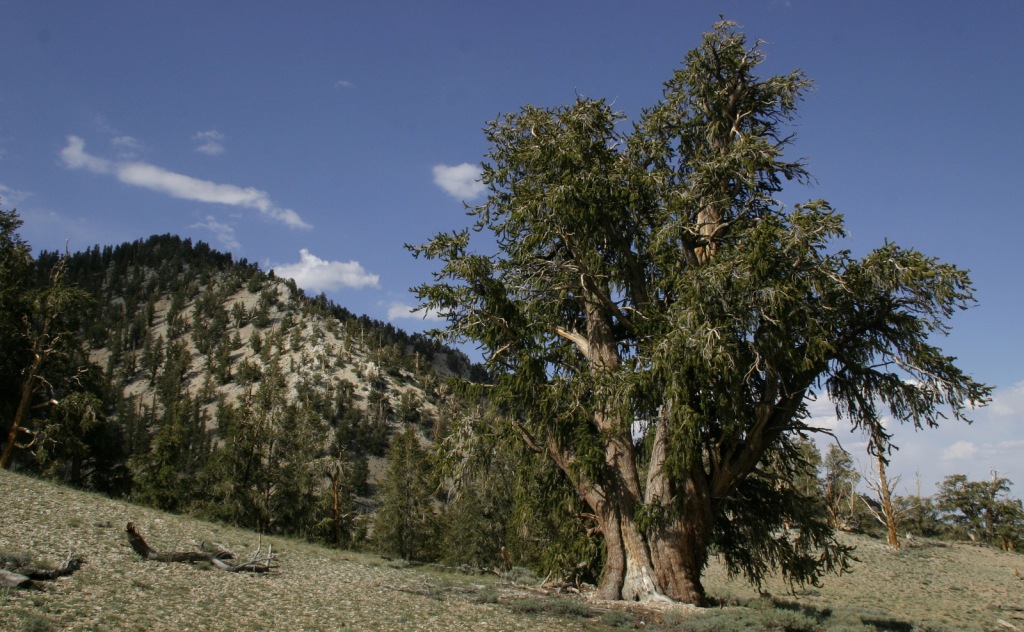
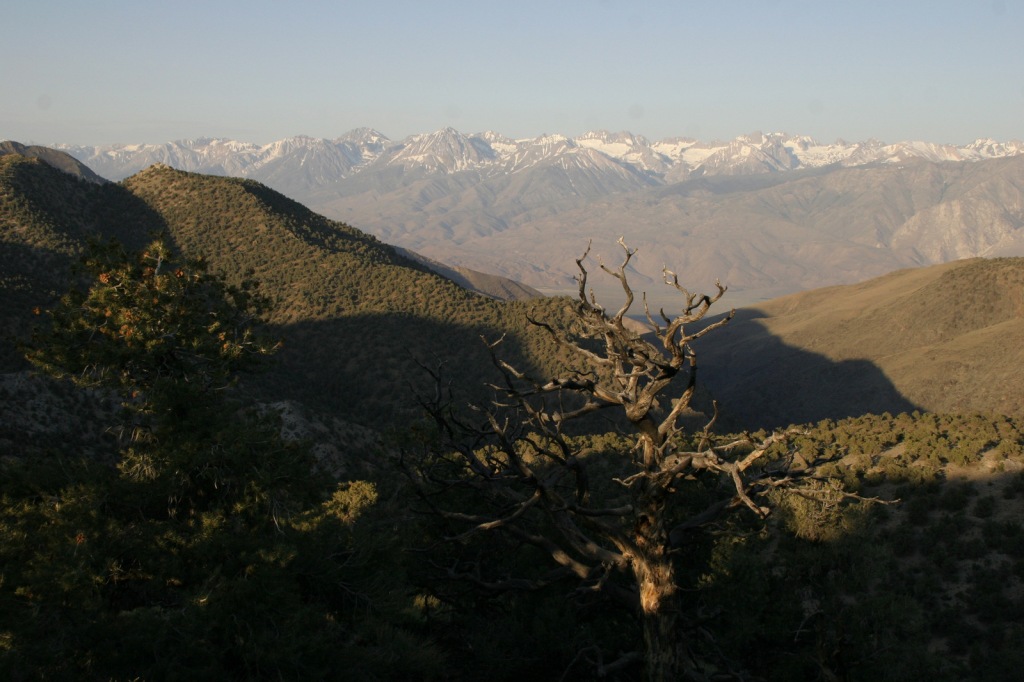
In the White Mountains, a paved road leads to the U.S. Forest Service visitor center at the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest, where a 4.5-mile loop trail through the Methuselah Grove passes one live Great Basin bristlecone pine tree recorded at over 5,000 years of age. That ranks it as the oldest living single-stem tree on the planet based on annual tree-ring measurements. You can continue to drive above 11,000 feet in elevation along a narrow gravel road famous for puncturing tires (so bring a spare). The route offers awesome views of the Owens Valley and Mt. Whitney, then takes you to the Patriarch Grove, a wonderful park of gnarled Great Basin bristlecone pine trees surrounded by snow throughout the summer.
Best Trail
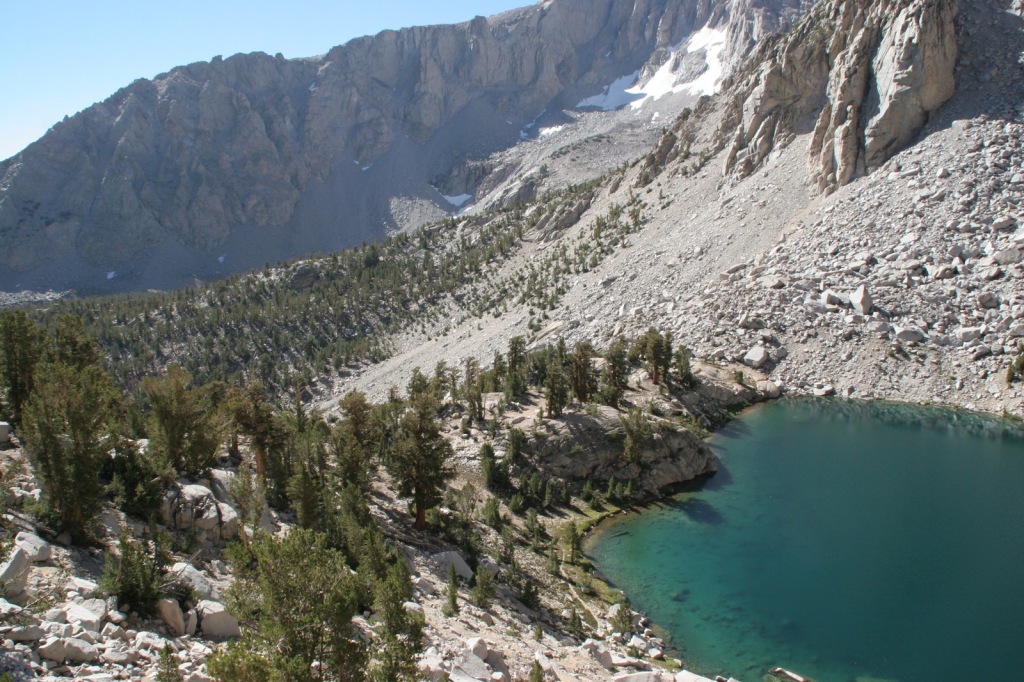
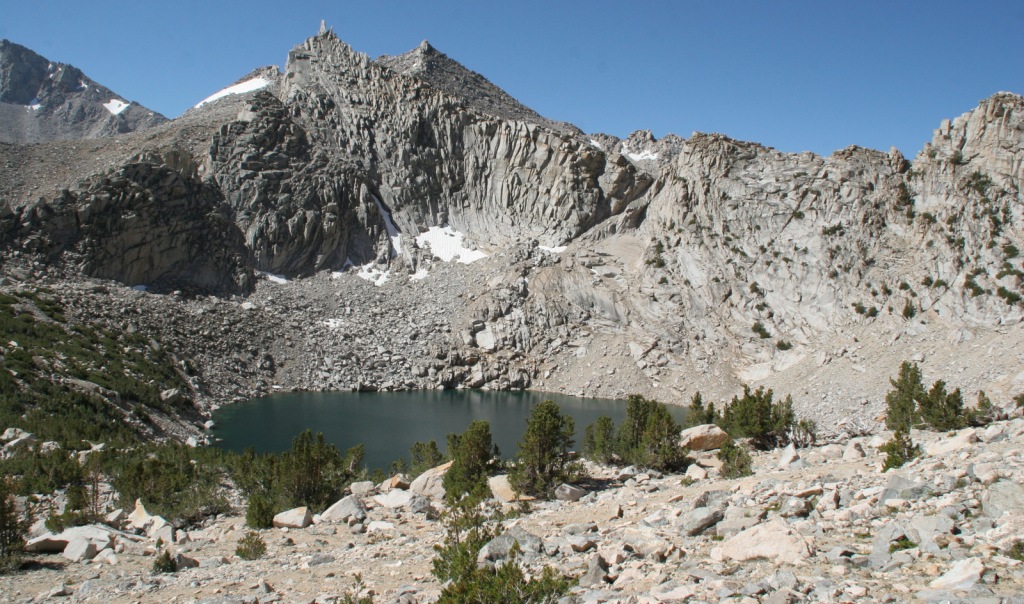
Onion Valley Road west of Independence dead ends at the trailhead for Kearsarge Pass in the Sierra Nevada. The trail is a series of endless switchbacks that lead past beautifully twisted foxtail pines and unbelievably blue lakes up to the 11,823-foot pass at the boundary with Kings Canyon National Park. The view from the pass is worth the effort, even if you do not proceed to enter the National Park, for which you need a permit to camp overnight. John Muir called these mountains “the range of light,” and from up here you will surely see why.
Watchable Wildlife
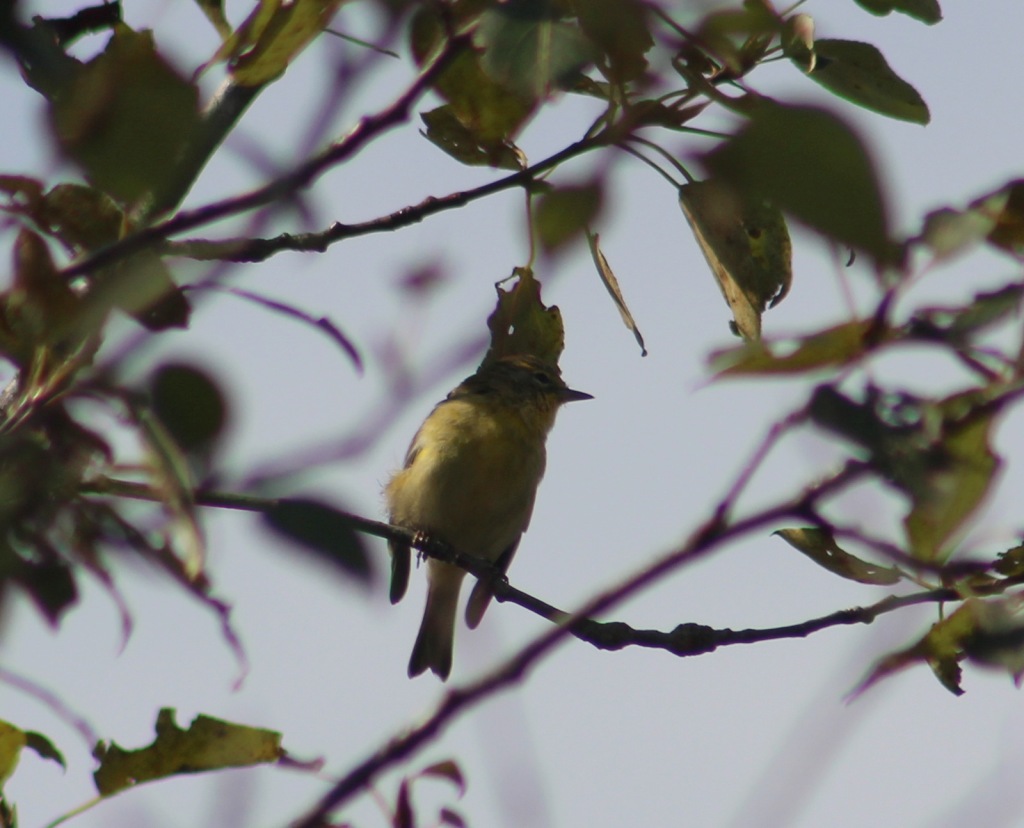
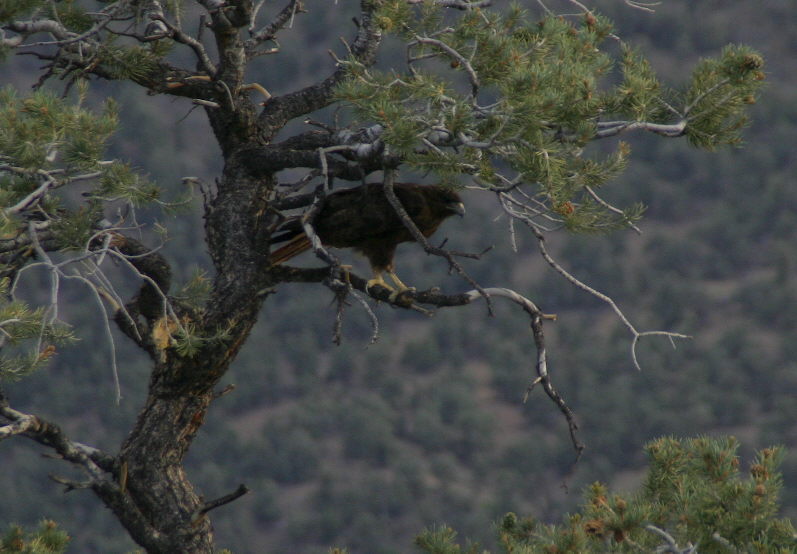
Inyo National Forest is on the rain-shadow side of the Sierra Nevada, so it generally receives less precipitation throughout the year than the western slopes, especially at lower elevations. In the conifer forests of the mountains look for mule deer, black bears, weasels, martens, mountain lions, and bobcats. California quail, mountain quail, sooty grouse, and wild turkeys are common game birds. Watch the skies for raptors like bald eagles, ospreys, red-tailed hawks, and turkey vultures.
Instagram-worthy Photo
Sun-streaked and wind-blasted branches of bristlecone pine trees twist in backbreaking curls, stretching up towards the deep blue skies above 10,000 feet elevation.

Peak Season
Summer
Fees
There are no day use fees to our knowledge.
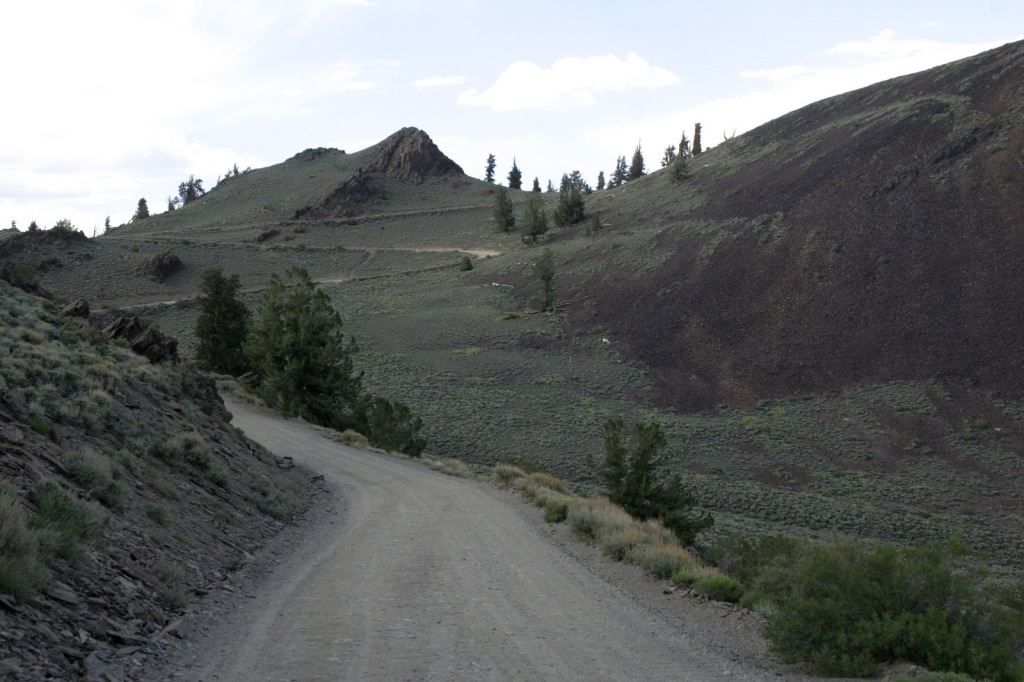
Road Conditions
The road is paved to the trailhead for the 4.5-mile loop through the Methuselah Grove in the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest. The unpaved road beyond is famous for puncturing tires (so take it slow and bring a spare) and retains snow late into the summer. A shuttle ticket or camping permit is required to drive into the National Forest west of the ski resort town of Mammoth Lakes to access Devils Postpile National Monument.
Camping
Grandview Campground near the Ancient Bristlecone Pine Forest lives up to its name. There is a campground at Whitney Portal Trailhead and two on Onion Valley Road on the way to the trailhead for Kearsarge Pass (plus some epic dispersed campsites).
Wilderness Areas
Ansel Adams Wilderness (also in Sierra National Forest and Devils Postpile National Monument)
Boundary Peak Wilderness
Golden Trout Wilderness (also in Sequoia National Forest)
Hoover Wilderness (also in Toiyabe National Forest)
Inyo Mountains Wilderness
John Muir Wilderness (also in Sierra National Forest)
Owens River Headwaters Wilderness
South Sierra Wilderness (also in Sequoia National Forest)
White Mountains Wilderness
Related Sites
Humboldt National Forest (Nevada)
Yosemite National Park (California)
Manzanar National Historic Site (California)
Nearest National Park
Kings Canyon




























Great Basin bristlecone pine, foxtail pine, Jeffrey pine, ponderosa pine, lodgepole pine, Douglas-fir, California red fir, white fir, incense-cedar
quaking aspen, greenleaf manzanita, sagebrush
Explore More – What 1973 film starring Clint Eastwood was filmed in Inyo National Forest?

Learn more about this and the 154 other National Forests in our new guidebook Out in the Woods